خرید گزارش Paint and Coatings Industry Overview از Chemical Economics Handbook

خرید گزارش Paint and Coatings Industry Overview
برای دانلود فایل Paint and Coatings Industry Overview مربوط به Chemical Economics Handbook و دریافت پی دی اف بررسی اجمالی صنعت رنگ و روکش بر روی کلید خرید در انتهای صفحه کلیک کنید. پس از اتصال به درگاه پرداخت و تکمیل مراحل خرید، لینک دانلود ایمیل می شود. این گزارش مربوط به سال 2019 و در فرمت PDF ارسال می شود.
در صورتی که نیاز به دانلود هر گزارشی از IHS و یا PEP دارید، فقط کافیست ادرس اینترنتی گزارش را از سایت ihsmarkit.com و یا https://global.ihs.com برای ما ارسال کنید (راههای ارتباطی در صفحه تماس با گیگاپیپر ). پس از بررسی، هزینه ان اعلام می شود. پس از واریز نسخه الکترونیکی ارسال می شود.
Paint and Coatings Industry Overview
Chemical Economics Handbook
Published April 2019
For Download Please Contact Us :
Price : 55$
دانلود رایگان گزارش Paint and Coatings Industry Overview
برای اطمینان از کیفیت گزارش Paint and Coatings Industry Overview، چند صفحه ابتدایی ان بصورت رایگان قرار داده شده است.گزارشهای دیگر دانلودی از ihsmarkit.com به همین صورت هستند.
درباره گزارش Paint and Coatings Industry Overview
The coatings industry is one of the most heavily regulated industries in the world, so producers have been forced to adopt low-solvent and solventless technologies in the past 40 years, and will continue to do so. The number of coatings producers is large, but most are regional producers, with only 10 or so large multinationals; however, most of the large multinationals have expanded operations in fast-growing areas like China and India. The most noteworthy trend has been consolidation, especially among the largest producers.
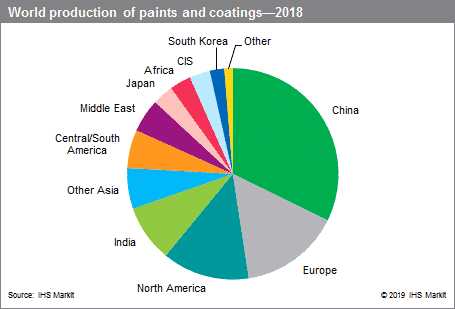
The following pie chart shows world production of paints and coatings:
Production and consumption are nearly equal in each country, as trade is limited to relatively small quantities of highvalue product. Demand in Asia continues to rise faster than elsewhere in the world, and the region now accounts for 50–55% of global consumption on a volume basis. Generally, coatings grow in tandem with the economy, so growth will continue to focus on the developing world.
Coatings provide two primary functions that are of considerable economic importance—decoration and protection. About 55% of the coatings produced worldwide are used to decorate and protect new construction as well as to maintain existing structures, including residential homes and apartments, public buildings, and plants and factories. Another 35% of the coatings are used to decorate and/or protect industrial products. Without coatings, product lives might be shortened drastically and many products would not even be marketable. Most of the remaining coatings, called “special purpose,” are used for miscellaneous applications such as traffic paints, vehicle refinishing, high-performance coatings for industrial plants and equipment, and protection of marine structures and vessels.
The coatings industry in the United States, Western Europe, and Japan is mature and generally reflects the health of the economy, especially housing, construction, and transportation. Overall demand from 2018 to 2023 will increase at average annual rates of 2% in the United States and 1.5–2.0% in Western Europe, with little to no growth expected in Japan.
In emerging countries, coatings are growing at a much faster rate. The best prospects for growth are in China (5–6% average annual growth), India (6%), Poland (3–4%), and Saudi Arabia (4.0–4.5%). Total global growth should be about 4% per year. On a value basis, it is likely that growth will be even higher as a result of the increased production of relatively higher-value coatings. Most of the major multinational coatings producers have production in China. The multinational producers should gain even more presence in the developing world as living standards increase and per capita consumption of coatings rises.
The major change that has taken place in the coatings industry during the last 40 years has been the adoption of new coating technologies. These new coating technologies include waterborne (thermosetting emulsion, colloidal dispersion, water-soluble) coatings, high-solids coatings, two-component systems, powder coatings, and radiation-curable coatings. Through the next five years, air pollution regulations will continue to be a driving force behind the adoption of new coating technologies; however, consumer preference is having a larger effect. For the architectural coatings market, waterbornes will likely continue to grow as consumers demand coatings that are free from odors and potentially hazardous raw materials.
In general, environmental regulations are becoming more stringent in all regions to limit emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs), not only in the industrialized world, but also in developing countries like China. Energy conservation and rising solvent and raw material costs are also contributing factors; raw material costs account for 50–60% of the total production costs for coatings. The coatings industry is one of the larger consumers of solvents, which are mostly derived from petrochemical feedstocks and refinery operations. The coatings industry also uses a considerable quantity of nonpetrochemical feedstocks, such as pigments and additives, which are not very dependent on crude oil and gas prices. The nonpetrochemical portion of the feedstocks is approximately one-third, on a volume basis.
One area of interest is nanotechnology, with tens of thousands of patents issued already just for the coatings industry. Very small ceramic or metallic particles can be added to paint formulations to modify specific properties (e.g., scratch, mar, wear, corrosion, and UV resistance) in highly specialized applications. The average size of nanoparticles is 10–70 nanometers, consisting of less than 6.5 million atoms. At these sizes, the ratio of surface area to mass becomes significant, giving the particles unique properties. For example, at 2 nanometers, the conductivity of metal particles changes and at 20 nanometers, the transparency of ceramic particles changes. At 20 nanometers, particles of gold turn red and their plasticity disappears.
دانلود گزارش بررسی اجمالی صنعت رنگ و روکش
صنعت روکش یکی از صنایع بسیار سنگین و مرتب در جهان است ، بنابراین تولیدکنندگان در 40 سال گذشته مجبور شده اند فن آوری های کم حل و حلال را اتخاذ کنند و این کار را ادامه خواهند داد. تعداد تولید کنندگان پوشش بسیار زیاد است ، اما بیشتر آنها تولیدکننده منطقه هستند و تنها 10 یا چند ملیت بزرگ دارند. با این حال ، بسیاری از چند ملیتی بزرگ عملیات را در مناطقی با رشد سریع مانند چین و هند گسترش داده اند. قابل توجه ترین روند ادغام ، خصوصاً در بین بزرگترین تولید کنندگان است.
نمودار پای زیر تولید رنگ و روکش جهانی را نشان می دهد:
تولید و مصرف تقریباً در هر کشور مساوی است ، زیرا تجارت محدود به مقادیر نسبتاً کمی از محصول پر ارزش است. تقاضا در آسیا سریعتر از سایر نقاط جهان افزایش می یابد ، و این منطقه در حال حاضر 50 تا 55٪ از مصرف جهانی را به صورت حجم تشکیل می دهد. به طور کلی ، پوشش ها با اقتصاد همگام می شوند ، بنابراین رشد تمرکز خود را بر جهان در حال توسعه ادامه خواهد داد.
روکش ها دو عملکرد اصلی را ارائه می دهند که از اهمیت اقتصادی قابل توجهی برخوردارند – تزئینات و محافظت. حدود 55٪ از روکش های تولید شده در سراسر جهان برای تزئین و محافظت از ساخت و سازهای جدید و همچنین برای حفظ سازه های موجود از جمله خانه های مسکونی و آپارتمان ها ، ساختمانهای عمومی و گیاهان و کارخانه ها استفاده می شود. 35٪ دیگر از روکش ها برای تزئین و / یا محافظت از محصولات صنعتی استفاده می شود. بدون پوشش ، عمر محصولات ممکن است به شدت کاهش یابد و بسیاری از محصولات حتی قابل فروش هم نباشند. بیشتر پوشش های باقیمانده به نام “هدف ویژه” برای مصارف مختلف مانند رنگ ترافیکی ، پالایش خودرو ، پوشش های با کارایی بالا برای کارخانه ها و تجهیزات صنعتی و محافظت از سازه های دریایی و کشتی ها استفاده می شوند.
صنعت روکش در ایالات متحده ، اروپای غربی و ژاپن بالغ است و به طور کلی بازتاب سلامت اقتصاد به ویژه مسکن ، ساخت و ساز و حمل و نقل است. تقاضای کلی از سال 2018 تا 2023 با متوسط نرخ سالانه 2٪ در ایالات متحده و 1.5-2.0٪ در اروپای غربی افزایش می یابد ، با رشد اندکی یا بدون رشد در ژاپن انتظار می رود.
در کشورهای در حال ظهور ، پوشش ها با سرعت بسیار بیشتری رشد می کنند. بهترین چشم انداز برای رشد در چین (متوسط رشد سالانه 5-6٪) ، هند (6٪) ، لهستان (4-4٪) و عربستان سعودی (4/4 تا 5/5 درصد) است. رشد کل جهانی باید در حدود 4٪ در سال باشد. بر مبنای ارزش ، احتمالاً به دلیل افزایش تولید روکشهای با ارزش نسبتاً بالاتر ، رشد حتی بیشتر خواهد شد. بیشتر تولید کنندگان عمده پوشش های چند ملیتی در چین تولید دارند. با افزایش استانداردهای زندگی و افزایش سرانه پوشش پوشش ، تولیدکنندگان چند ملیتی باید در جهان در حال توسعه حضور بیشتری کسب کنند.
تغییر عمده ای که در 40 سال گذشته در صنعت پوشش رخ داده است ، پذیرش فن آوری های جدید پوشش است. این فن آوری های جدید پوشش شامل پوشش های ضد آب (پوشش امولسیون گرمایی ، پراکندگی کلوئیدی ، محلول در آب) ، پوشش های جامد بالا ، سیستم های دو جزء ، روکش های پودری و روکش های قابل اشعه است. طی پنج سال آینده ، مقررات مربوط به آلودگی هوا به عنوان محرک اصلی اتخاذ فناوریهای جدید پوشش خواهد بود. با این حال ، اولویت مصرف کننده تأثیر بیشتری دارد. برای بازار پوشش های معماری ، احتمالاً با توجه به اینکه مصرف کنندگان خواستار پوشش هایی هستند که عاری از بو و مواد خام بالقوه خطرناک نباشند ، رشد می یابد.
به طور کلی ، مقررات زیست محیطی در همه مناطق سختگیرتر می شوند تا انتشار آلاینده های آلی فرار (VOC) و آلاینده های هوا خطرناک (HAPs) محدود شود ، نه تنها در جهان صنعتی بلکه در کشورهای در حال توسعه مانند چین. صرفه جویی در مصرف انرژی و بالا رفتن هزینه های حلال و مواد اولیه نیز عوامل مؤثر هستند. هزینه های مواد اولیه 50-60 of از کل هزینه های تولید پوشش ها را تشکیل می دهند. صنعت روکش یکی از مصرف کنندگان بزرگ حلالها است که بیشتر از منابع خوراکی پتروشیمی و عملیات پالایشگاه حاصل می شود. در صنعت پوشش نیز از مقدار قابل توجهی از خوراکهای غیرپتروشیمی مانند رنگدانه ها و مواد افزودنی استفاده می شود که به قیمت نفت خام و بنزین بسیار وابسته نیستند. بخش غیر پتروشیمیایی مواد خوراکی تقریباً یک سوم و به صورت حجمی است.
یکی از مناطق مورد علاقه ، فناوری نانو است که ده ها هزار اختراع ثبت شده در حال حاضر فقط برای صنعت پوشش ارائه می شود. ذرات سرامیکی یا فلزی بسیار کوچک را می توان به فرمول های رنگی اضافه کرد تا خصوصیات خاصی (به عنوان مثال ، خراش ، مار ، ساییدگی ، خوردگی و مقاومت در برابر اشعه ماوراء بنفش) در برنامه های بسیار تخصصی اصلاح شود. اندازه متوسط نانوذرات 10-70 نانومتر است که کمتر از 6.5 میلیون اتم تشکیل شده است. در این اندازه ها ، نسبت سطح سطح به جرم قابل توجه می شود و به ذرات خاصیت منحصر به فردی می بخشد. به عنوان مثال ، در 2 نانومتر ، هدایت ذرات فلزی تغییر می کند و در 20 نانومتر شفافیت سرامیک را نشان می دهد
Download Paint and Coatings Industry Overview
Contents