دانلود گزارش Hydrogen از Chemical Economics Handbook

خرید گزارش Hydrogen
برای دانلود فایل Hydrogen مربوط به Chemical Economics Handbook و دریافت پی دی اف بررسی اجمالی صنعت پتروشیمی بر روی کلید خرید در انتهای صفحه کلیک کنید. پس از اتصال به درگاه پرداخت و تکمیل مراحل خرید، لینک دانلود ایمیل می شود. این گزارش مربوط به سال 2018 و در فرمت PDF ارسال می شود.
در صورتی که نیاز به دانلود هر گزارشی از IHS و یا PEP دارید، فقط کافیست ادرس اینترنتی گزارش را از سایت ihsmarkit.com و یا https://global.ihs.com برای ما ارسال کنید (راههای ارتباطی در صفحه تماس با گیگاپیپر ). پس از بررسی، هزینه ان اعلام می شود. پس از واریز نسخه الکترونیکی ارسال می شود.
Hydrogen
Chemical Economics Handbook
Published May 2018
لینک گزارش از Chemical Economics Handbook:
For Download Please Contact Us :
Price : 55$
دانلود رایگان گزارش Hydrogen
برای اطمینان از کیفیت گزارش Hydrogen ، چند صفحه ابتدایی ان بصورت رایگان قرار داده شده است.گزارشهای دیگر دانلودی از ihsmarkit.com به همین صورت هستند.
درباره گزارش Hydrogen
Hydrogen is produced in large quantities both as a principal product and as a by-product. Hydrogen producers may consume the product captively, sell it to end users, sell it to a company that specializes in marketing industrial gases, burn it for fuel, or vent it to the atmosphere. Hydrogen consumers may buy hydrogen from an industrial gas company or a byproduct producer, use internally generated by-product hydrogen or install a hydrogen plant on-site. In some cases, a company will generate crude by-product hydrogen that is purchased and purified by an industrial gas company and then sold back to the original generating company.
Growth in the hydrogen market is driven primarily by regulations pertaining to desulfurization of fuel used in transportation, growth in transportation fuels, and a decrease in crude quality, requiring more and more hydrogen for processing. Hydrogen generation from crude processing is also decreasing because of poor-quality crudes. This has caused refineries to look for hydrogen availability from merchant sources that are set up on-site or adjacent to the refining facilities. The Middle East is expected to process huge volumes of sour natural gas that require significantly higher quantities of hydrogen to adhere to environmental standards. There is also rising demand for distillate fuels that would require increased hydrogen consumption.
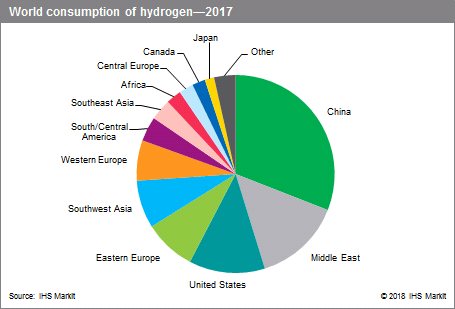
The following pie chart shows world consumption of hydrogen:
Higher growth rates are expected in China as a result of high levels of urban pollution leading to efforts to reduce emissions by enforcing stricter fuel sulfur regulation. BRIC economies, including India and Russia, are also planning to export ultra-low-sulfur fuels, thereby increasing hydrogen consumption in those regions. Though Western Europe and Japan have stagnant markets, North America is expected to increase hydrogen consumption mostly because of the abundant petroleum feedstock supply and advanced technologies.
Nearly 96% of all hydrogen is derived from fossil fuels, with natural gas being by far the most frequently used with an estimated 49%, followed by liquid hydrocarbons at 29%, 18% from coal, and about 4% from electrolysis and other byproduct sources of hydrogen.
Steam reforming of coal and steam reforming of natural gas are two major methods for producing large volumes of hydrogen in China, where hydrogen produced by these two methods is used mainly in the production of ammonia and methanol. Ammonia, petroleum refining, and methanol are the three largest individual markets for hydrogen in China, accounting for over 93% of China’s total hydrogen consumption in 2017.
Global opportunities for hydrogen look strong in the forecast period. Production of ammonia has been on the rise, especially in the United States, with lower natural gas prices providing an advantage. The methanol market is also experiencing robust growth. Demand for distillate is steadily on the increase. Refineries are large-volume producers and consumers of hydrogen for distillate. In general, environmental regulations implemented in most industrialized countries result in increased hydrogen requirements at refineries for gasoline and diesel desulfurization because of increased demand for cleaner fuels and tighter engine manufacturer specifications.
In addition, ongoing oil sands processing, gas-to-liquids, and coal gasification projects all require enormous amounts of hydrogen and will boost the size of the market significantly in the next five years. Alberta, Canada has an enormous area containing oil sands that can be processed to produce oil. Even by conservative estimates, this area is estimated to be the second-largest oil reserve after Saudi Arabia. Desulfurization operations for these sands would consume vast quantities of hydrogen.
Hydrogen is also expected to see a surge in consumption in the manufacture of methanol. Substantial methanol consumption in direct-fuel use as motor gasoline is expected in countries such as China, Russia, South Africa, Venezuela, and several Middle Eastern countries.
Overall global demand for hydrogen is expected to increase at around 4–5% per year during the next five years, primarily as a result of demand from petroleum refinery operations, and the production of ammonia and methanol. Asia will continue to lead demand growth in line with the increasing growth of its domestic economies.
دانلود گزارش بررسی اجمالی صنعت پتروشیمی
هیدروژن در مقادیر زیادی هم به عنوان یک محصول اصلی و هم به عنوان یک محصول جانبی تولید می شود. تولیدکنندگان هیدروژن ممکن است این محصول را به صورت اسیر مصرف کنند ، آن را به کاربران نهایی بفروشند ، آن را به شرکتی که در بازاریابی گازهای صنعتی تخصص دارد ، بفروشند ، آن را برای سوخت یا سوختن آن به جو بفروشند. مصرف كنندگان هیدروژن ممكن است هیدروژن را از یك شركت گاز صنعتی یا تولید كننده فرعی تولید كنند ، از هیدروژن جانبی محصول داخلی استفاده كنند یا كارخانه هیدروژن را در محل نصب كنند. در بعضی موارد ، یک شرکت هیدروژن جانبی فرآورده خام تولید می کند که توسط یک شرکت گاز صنعتی خریداری و تصفیه می شود و دوباره به شرکت تولید کننده اصلی فروخته می شود.
رشد در بازار هیدروژن در درجه اول با مقررات مربوط به نمك زدایی سوخت مورد استفاده در حمل و نقل ، رشد سوخت های حمل و نقل و كاهش كیفیت خام انجام می شود كه نیاز به هیدروژن بیشتر و بیشتر برای فرآوری دارد. تولید هیدروژن حاصل از فرآوری نفت خام نیز به دلیل خام های بی کیفیت در حال کاهش است. این امر باعث شده است كه پالایشگاه ها به دنبال دسترسی هیدروژن از منابع تجارتی باشند كه در محل یا در مجاورت تأسیسات پالایش قرار دارند. انتظار می رود خاورمیانه حجم زیادی از گاز طبیعی ترش را پردازش کند که نیاز به مقادیر قابل توجهی هیدروژن برای رعایت استانداردهای زیست محیطی دارد. همچنین افزایش تقاضا برای سوختهای تقطیر شده که نیاز به افزایش مصرف هیدروژن دارند ، وجود دارد.
نمودار پای زیر مصرف جهانی هیدروژن را نشان می دهد:
انتظار می رود نرخ رشد بالاتر در چین به دلیل سطح بالای آلودگی شهری منجر به تلاش برای کاهش تولید گازهای گلخانه ای با اجرای دقیق تر تنظیم گوگرد سوخت شود. اقتصادهای بریک از جمله هند و روسیه نیز قصد صادرات سوخت های بسیار کم گوگرد را دارند و از این طریق میزان مصرف هیدروژن در آن مناطق افزایش می یابد. گرچه اروپای غربی و ژاپن از بازارهای راکد برخوردار هستند ، اما انتظار می رود که آمریکای شمالی مصرف هیدروژن را بیشتر بخاطر عرضه فراوان خوراک نفت و فناوریهای پیشرفته افزایش دهد.
تقریباً 96٪ از کل هیدروژن ها از سوخت های فسیلی حاصل می شوند که گاز طبیعی بیشترین استفاده آنها با تخمین 49٪ است و پس از آن هیدروکربن های مایع با 29٪ ، 18٪ از زغال سنگ و حدود 4٪ از الکترولیز و سایر فرآورده های جانبی. منابع هیدروژن.
اصلاح بخار از زغال سنگ و اصلاح بخار گاز طبیعی دو روش اصلی برای تولید حجم زیادی از هیدروژن در چین است ، جایی که هیدروژن تولید شده توسط این دو روش عمدتاً در تولید آمونیاک و متانول استفاده می شود. آمونیاک ، پالایش نفت و متانول سه بازار بزرگ هیدروژن در چین است که بیش از 93٪ کل مصرف هیدروژن چین در سال 2017 را تشکیل می دهد.
فرصت های جهانی هیدروژن در دوره پیش بینی بسیار قوی به نظر می رسد. تولید آمونیاک بویژه در ایالات متحده رو به افزایش بوده است و قیمت گاز طبیعی پایین تر مزیت آن را فراهم می کند. بازار متانول نیز رشد قوی را تجربه می کند. تقاضا برای تقطیر به طور پیوسته در حال افزایش است. پالایشگاه ها تولیدکننده و مصرف کننده بزرگی از هیدروژن برای تقطیر هستند. به طور کلی ، مقررات زیست محیطی که در اکثر کشورهای صنعتی اعمال می شود منجر به افزایش نیاز هیدروژن در پالایشگاههای بنزین و دیزل زدایی به دلیل افزایش تقاضا برای سوختهای تمیزتر و مشخصات تولیدکنندگان محکمتر می شوند.
علاوه بر این ، پروسه های مایع در حال پردازش ماسه های نفتی ، گازهای مایع و پروژه های گازرسانی زغال سنگ ، همگی به مقادیر زیادی هیدروژن احتیاج دارند و باعث افزایش چشمگیر بازار در 5 سال آینده می شوند. آلبرتا ، کانادا دارای منطقه عظیم و حاوی ماسه های روغنی است که می توانند برای تولید روغن فرآوری شوند. حتی با برآورد محافظه کارانه ، این منطقه پس از عربستان سعودی دومین ذخیره نفتی محسوب می شود. عملیات نمک زدایی برای این ماسه ها مقدار زیادی هیدروژن مصرف می کند.
همچنین انتظار می رود هیدروژن شاهد افزایش مصرف در تولید متانول باشد. در کشورهایی مانند چین ، روسیه ، آفریقای جنوبی ، ونزوئلا و چندین کشور خاورمیانه انتظار می رود مصرف قابل توجهی متانول در مصرف سوخت مستقیم به عنوان بنزین موتور پیش بینی شود.
انتظار می رود تقاضای جهانی هیدروژن در طی 5 سال آینده حدود 4 تا 5 درصد در سال افزایش یابد ، در درجه اول به عنوان نتیجه تقاضای عملیات پالایشگاه نفت و تولید آمونیاک و متانول. آسیا همگام با رشد روزافزون اقتصادهای داخلی ، منجر به رشد تقاضا خواهد شد.
Download Hydrogen
Table of Contents
SectionPage Number
Executive summary7
Introduction13
Properties, grades, and form of supply14
Manufacturing processes16
Production processes16
Steam reforming of hydrocarbons16
Dissociation of hydrocarbons20
Electrolysis22
Other24
By-product generation24
New developments27
Hydrogen use as a primary energy source31
Supply and demand by region35
United States35
Producing companies35
Merchant hydrogen producers35
Liquid hydrogen producers35
Gaseous hydrogen producers37
Pipeline systems46
Captive hydrogen producers52
By-product hydrogen producers59
Production62
Consumption62
Petroleum refining64
Hydrogen production67
Hydrogen consumption68
Chemicals69
Metals73
Electronics74
Edible fats and oils75
Government77
Public utilities79
Cooling79
Corrosion prevention79
Float glass82
Other84
Price85
Trade87
Canada90
Producing companies90
Merchant hydrogen producers90
Liquid hydrogen producers90
Gaseous hydrogen producers90
Pipeline systems91
Captive hydrogen producers93
By-product hydrogen producers94
Consumption96
Trade97
Mexico99
Producing companies99
Salient statistics102
Trade102
Central and South America103
Western Europe106
Producing companies108
Merchant hydrogen producers108
Liquid hydrogen producers108
Gaseous hydrogen producers109
Pipeline systems115
Captive hydrogen producers120
By-product hydrogen producers126
Production capacity133
Production135
Consumption138
Gaseous hydrogen141
Ammonia141
Petroleum refining141
Methanol142
Metals production142
Aniline142
Hydrogen peroxide142
Oxo chemicals143
Cyclohexane143
Toluene diisocyanate—TDI143
Fats and oils143
Hexamethylenediamine—HMDA143
Hydrochloric acid143
Fatty alcohols143
Caprolactam143
1,4-Butanediol—BDO144
Float glass144
Transportation/hydrogen projects144
Electronics146
Adipic acid147
Liquid hydrogen147
Space industry147
Fuel147
Semiconductors and thin-film solar148
Price148
Trade149
Central Europe151
Producing companies151
Merchant gaseous hydrogen producers151
Captive hydrogen producers152
By-product hydrogen producers154
Production capacity155
Production156
Consumption158
Ammonia159
Petroleum refining159
Methanol159
Eastern Europe160
Producing companies160
Merchant gaseous hydrogen producers160
Captive hydrogen producers160
By-product hydrogen producers162
Production capacity164
Production165
Consumption166
Ammonia167
Petroleum refining167
Methanol167
Gas-to-liquids (GTL)168
Middle East168
Producing companies168
Merchant gaseous hydrogen producers168
Captive hydrogen producers169
By-product hydrogen producers171
Production capacity173
Production175
Consumption176
Ammonia178
Gas-to-liquids (GTL)178
Petroleum refining178
Methanol178
Africa178
Producing companies178
Merchant gaseous hydrogen producers178
Captive hydrogen producers179
By-product hydrogen producers180
Production capacity181
Production183
Consumption184
Ammonia185
Gas-to-liquids (GTL)185
Petroleum refining185
Methanol185
Southwest Asia186
Producing companies186
Salient statistics188
Bangladesh188
India188
Pakistan188
Consumption188
Trade189
China190
Producing companies190
Production198
Consumption200
Chemicals200
Ammonia200
Methanol200
Hydrochloric acid201
Hydrogen peroxide201
Aniline201
Cyclohexane201
Caprolactam201
n-Butanol201
2-Ethylhexyl alcohol201
1,4-Butanediol201
Hexamethylenediamine—HMDA201
Petroleum refining202
Float glass202
Metals203
Fats and oils203
Electronics203
Other204
Price204
Trade204
Japan207
Producing companies207
Merchant hydrogen producers207
Liquid hydrogen producers207
Gaseous hydrogen producers208
Captive hydrogen producers210
Hydrogen fuel cell filling stations211
Production212
Consumption213
Electronics214
Metals214
Fats and oils214
Glass215
Price215
Trade215
Other Asia216
Northeast Asia216
Producing companies216
Salient statistics218
South Korea218
Taiwan219
Consumption219
Southeast Asia220
Producing companies220
Salient statistics223
Consumption223
Trade224
Oceania225
Producing companies225
Salient statistics226
Australia226
New Zealand226
Consumption226
Trade226
Appendix228
Bibliography229
Revisions230